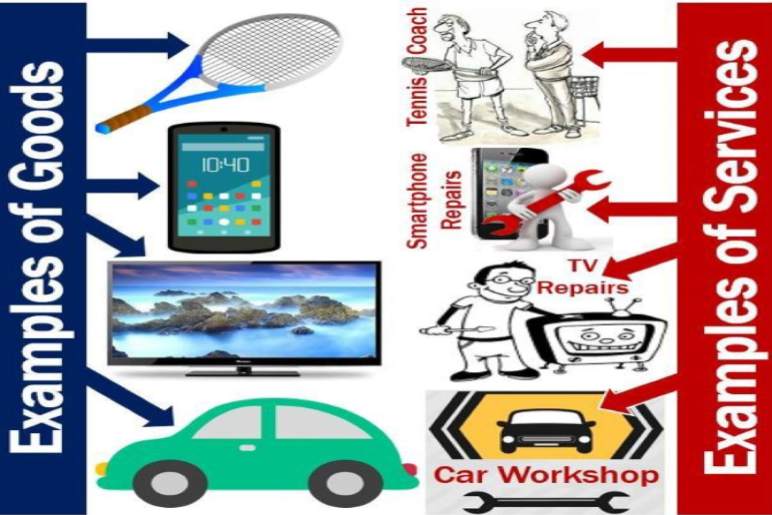
Services are intangible activities or benefits that one party can offer to another. Unlike physical products, services are consumed at the time of delivery and don’t result in ownership. These actions or performances create value for the customer and are often exchanged for monetary compensation.
The Etymology of “Services”

The word “service” is ubiquitous in our modern world. From customer service to public services, it’s a term we encounter daily. But where did this word originate? Let’s delve into its etymology.
The word “service” stems from the Latin word “servitium,” meaning “slavery” or “bondage.” It might seem counterintuitive that a word with such negative connotations evolved into something so positive. However, the historical context provides clarity. In ancient Rome, slaves provided various services to their masters, from domestic chores to skilled labor.
Over time, the concept of service expanded beyond forced labor. The word began to encompass acts of helpfulness, assistance, and utility. It transitioned from denoting a relationship of servitude to one of providing value. Today, “service” signifies a voluntary act performed for the benefit of others.
The evolution of the word mirrors the societal changes that have occurred. While the original meaning carries a dark history, the modern interpretation of “service” represents progress and human cooperation. It is a testament to the adaptability of language and our ability to redefine words to reflect evolving values.
Unique Characteristics of Services

Unlike physical products, services possess distinct qualities that shape their delivery and consumption. Understanding these characteristics is crucial for businesses operating in the service sector.
Intangibility
Services cannot be touched, seen, or tasted before they are purchased. Unlike a product that can be inspected, consumers rely on factors like reputation, brand image, and word-of-mouth to evaluate a service. Marketers often use tangible cues or symbols to represent the intangible service. For instance, a luxurious hotel lobby can symbolize the quality of the accommodation.
Inseparability
Services are produced and consumed simultaneously. The service provider and the customer are often involved in the same process. This interaction directly impacts the service experience. For example, a haircut depends on the skills and personality of the hairstylist. Consequently, service quality can vary across different providers.
Variability
Service delivery can vary from one provider to another, or even from one time to another for the same provider. Factors like employee skills, customer behavior, and environmental conditions can influence service quality. Service businesses must strive for consistency to build customer trust and loyalty.
Perishability
Services cannot be stored for later consumption. Unlike products, which can be inventoried, services are lost if not utilized when offered. This characteristic necessitates careful capacity planning and demand management. For instance, an airline seat left unoccupied represents lost revenue.
These four characteristics—intangibility, inseparability, variability, and perishability—collectively distinguish services from products. Understanding these qualities is essential for businesses to develop effective marketing strategies, manage service delivery, and build strong customer relationships.
The Service Industry

The service industry is a broad category encompassing a vast array of businesses that primarily offer intangible products. Unlike the manufacturing sector which produces physical goods, service industries focus on providing actions, experiences, or benefits. These services are essential to modern life, contributing significantly to economic growth and employment.
Key Sectors of the Service Industry

- Professional Services: This sector includes legal, accounting, consulting, and financial advisory services. Professionals in these fields offer expertise and knowledge to individuals and businesses.
- Healthcare: A vital component of the service industry, healthcare encompasses medical treatment, dental care, nursing, and various healthcare support services.
- Retail: While often associated with product sales, retail also involves significant service components, including customer support, returns, and after-sales services.
- Hospitality: The hospitality industry focuses on providing accommodation, food, and entertainment services to travelers and tourists.
- Transportation and Logistics: This sector offers services related to the movement of people and goods, including airlines, shipping, and delivery services.
- Information Technology (IT): IT services encompass software development, hardware maintenance, network support, and cybersecurity.
- Education: Providing knowledge and skills development, the education sector is a crucial component of the service industry.
The Rise of the Service Economy
The global economy has witnessed a shift from manufacturing to services. This transformation is driven by several factors:
- Technological advancements: Innovations in technology have enabled the delivery of services more efficiently and effectively.
- Globalization: Increased international trade and communication have expanded the market for services.
- Consumer preferences: Consumers are increasingly demanding convenience, quality, and personalized experiences.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Services

Services are an integral part of our economy, offering a wide range of benefits. However, they also come with certain challenges. Let’s explore the pros and cons of services.
Advantages of Services
- Customization: Services can be tailored to meet specific customer needs and preferences. This level of customization is often difficult to achieve with physical products.
- Customer Interaction: Direct interaction between service providers and customers can foster strong relationships and loyalty.
- Economic Growth: The service sector is a major contributor to economic growth and job creation.
- Intangibility: Services don’t require physical inventory, reducing storage and handling costs.
- Rapid Deployment: Services can be implemented quickly, often without the need for extensive setup.
Disadvantages of Services
- Inconsistency: Service quality can vary depending on the service provider, making it challenging to maintain consistency.
- Perishability: Services cannot be stored, making it difficult to match supply with demand.
- Difficulty in Evaluating Quality: Assessing the quality of a service before consumption can be challenging due to its intangible nature.
- Customer Satisfaction: Maintaining high levels of customer satisfaction is crucial, as negative experiences can spread quickly through word-of-mouth.
- Pricing Challenges: Determining the appropriate price for a service can be complex due to its intangible nature and the difficulty in measuring value.
Understanding both the advantages and disadvantages of services is essential for businesses operating in this sector. By effectively managing these factors, companies can enhance customer satisfaction and achieve long-term success.
We Can’t Store Services: The Perishability of Service
Unlike tangible products that can be produced, stored, and sold at a later date, services possess a unique characteristic: perishability.
This means that services cannot be stored for future consumption. Once a service is delivered, it ceases to exist.
The Implications of Perishability
- Lost Opportunities: If a service is not utilized when offered, the opportunity is lost forever. For instance, an empty airline seat or an unsold concert ticket represents lost revenue.
- Capacity Management: Service providers must carefully manage their capacity to align with demand. Overstaffing or understaffing can lead to inefficiencies and customer dissatisfaction.
- Demand Forecasting: Accurate demand forecasting is crucial for service businesses.This helps in optimizing resource allocation and preventing overbooking or underutilization.
- Revenue Management: Dynamic pricing strategies are often employed to maximize revenue, especially in industries with fluctuating demand, such as hotels and airlines.
Overcoming the Challenges
While perishability is an inherent characteristic of services, businesses can implement strategies to mitigate its impact.These include:
- Demand Management: Using marketing and pricing strategies to influence customer demand.
- Capacity Adjustment: Flexing staffing levels or service offerings based on demand fluctuations.
- Revenue Management: Implementing pricing strategies that optimize revenue based on demand and capacity.
- Customer Relationship Management: Building strong customer relationships to encourage repeat business and referrals.
Conclusion

In essence, services are intangible activities or benefits provided by one party to another. Unlike products, services are consumed at the time of delivery and don’t involve ownership transfer. From professional expertise to personal care, services are integral to modern economies. Understanding the unique characteristics of services is crucial for businesses to deliver exceptional customer experiences and build lasting relationships.
Read more:
- Blueface Net Worth, Lifestyle And Updates In 2024
- Alternatives to Payday Loans: Exploring Your Options
- Benefits of Selling Your Decommissioned Data Center Equipment
Featured Image source: https://tinyurl.com/yu26atfn

