Media is simply the plural of “medium,” referring to the channels used to communicate information or data. It’s the bridge between creators and audiences, shaping how we perceive the world around us. From the ancient practice of storytelling to the digital age, media has evolved rapidly, influencing culture, politics, and our daily lives.
From Town Crier to Twitter: The Evolution of Media

The way we consume information has undergone a dramatic transformation. From the days of spoken word and town criers to the digital age of social media, the evolution of media has been nothing short of astonishing.
The Dawn of Mass Communication
The invention of the printing press marked a pivotal moment in media history. It democratized information, making it accessible to a wider audience. Newspapers, magazines, and books became the primary channels of communication. Radio and television followed, expanding reach and impact.
The Digital Revolution
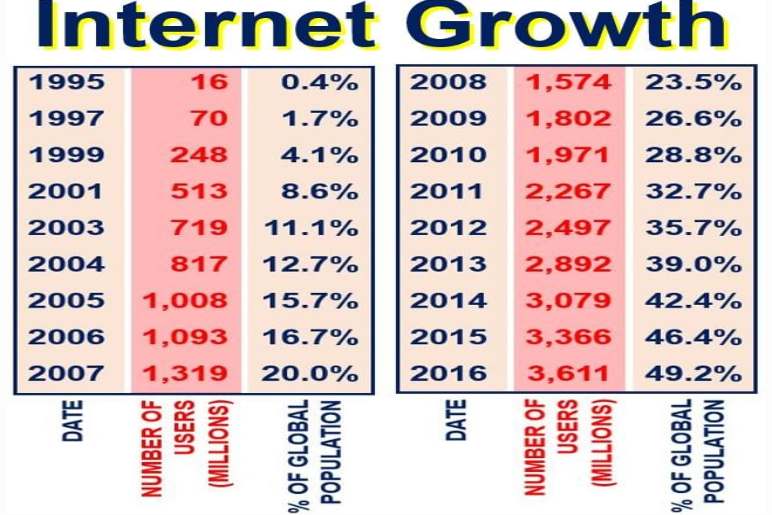
The internet ushered in a new era of media. The once one-way street of information transformed into a dynamic, interactive landscape. Websites, blogs, and online newspapers emerged, offering a wealth of information at our fingertips. Social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram revolutionized how we connect, share, and consume content.
The Impact of Digital Media
The digital revolution has had a profound impact on society. It has empowered individuals to become content creators, blurring the lines between consumer and producer. However, it has also brought challenges such as misinformation, privacy concerns, and the echo chamber effect.
The Future of Media
The media landscape continues to evolve rapidly. Virtual and augmented reality, artificial intelligence, and 5G technology are shaping the future. We can expect more immersive experiences, personalized content, and new forms of storytelling.
Types of Media: A World of Information

Media, in its simplest form, is the channel through which information is communicated. It’s evolved dramatically over time, from the spoken word to the digital age. Let’s explore some of the primary types of media:
Print Media
This is the oldest form of media, relying on physical paper to deliver information.
- Newspapers: Daily or weekly publications that cover news, features, and advertisements.
- Magazines: Periodical publications that often focus on specific topics or interests.
- Books: Bound collections of written or printed matter, offering in-depth knowledge and storytelling.
Broadcast Media
This type of media reaches a wide audience through electronic transmission.
- Television: Visual and auditory content delivered through airwaves or cable.
- Radio: Audio content transmitted through airwaves.
Digital Media
The internet revolutionized media consumption, leading to a vast array of digital formats.
- Websites: Online platforms offering information, services, and entertainment.
- Social Media: Platforms for social interaction and content sharing.
- Online Streaming: Delivering audio and video content over the internet.
- Mobile Apps: Software applications designed for smartphones and tablets.
Outdoor Media
This encompasses advertising and information displayed in public spaces.
- Billboards: Large outdoor advertising structures.
- Transit Advertising: Ads placed on public transportation.
- Digital Out-of-Home (DOOH): Electronic displays in public areas.
Media’s Role in Website Design: More Than Just Eye Candy

Media, encompassing images, videos, and audio, is far from being a mere aesthetic addition to website design. It’s a dynamic element that can significantly influence user experience, engagement, and overall website performance.
The Visual Impact
- First Impressions Matter: Images are the first things users notice. High-quality visuals can create a strong first impression, setting the tone for the entire website.
- Storytelling: Visuals can narrate a story, conveying information more effectively than text alone.
- Brand Identity: Consistent visual elements reinforce brand identity and recognition.
The Power of Audio
- Enhanced User Experience: Background music or sound effects can create a specific atmosphere, enhancing the overall user experience.
- Accessibility: Audio content can make websites more accessible to visually impaired users.
The Engagement Factor of Video
- Increased Time on Site: Videos can significantly increase time spent on a website.
- Improved SEO: Video content can improve search engine rankings.
- Explaining Complex Topics: Videos are excellent for explaining complex products or services.
Media Optimization for Performance
- Image Compression: Optimizing image size without compromising quality is crucial for fast loading times.
- Video Formats: Choosing the right video format ensures compatibility across different devices.
- Lazy Loading: Loading images and videos only when they are about to be seen improves page load speed.
Media and User Experience
- Emotional Connection: Media can evoke emotions, creating a stronger connection with the audience.
- Information Retention: Visual and audio content can improve information retention.
- Call to Action: Media can be used to encourage specific actions, such as making a purchase or signing up for a newsletter.
Media’s Impact on Society: A Double-Edged Sword

Media, in its various forms, has an undeniable influence on society. It shapes our opinions, values, and behaviors. While it can be a powerful tool for positive change, it also carries the potential for misinformation and negative impacts.
The Power of Influence
Media has the ability to set agendas, framing issues and determining what we prioritize. News outlets can shape public opinion, while advertising can influence consumer choices. Social media platforms have become echo chambers, reinforcing existing beliefs and limiting exposure to diverse perspectives.
Media and Culture
Media is a mirror reflecting society, but it also plays a role in shaping culture. Television shows, movies, and music influence fashion, language, and social norms. While this can lead to cultural exchange and diversity, it can also perpetuate stereotypes and unrealistic expectations.
The Dark Side
Despite its positive potential, media can also have negative impacts. The spread of misinformation and fake news can erode trust in institutions and fuel division. The constant pressure to maintain a perfect image on social media can lead to mental health issues. Moreover, the concentration of media ownership can limit diversity of voices and perspectives.
A Call for Media Literacy
To navigate the complex media landscape, media literacy is essential. It involves developing critical thinking skills to evaluate information, identify biases, and understand the impact of media on individuals and society. By becoming informed and discerning consumers of media, we can harness its power for positive change.
Understanding Media Ethics and Regulation

The media landscape is a dynamic ecosystem where information is produced, consumed, and shared at an unprecedented pace. As this landscape evolves, so too do the ethical considerations and regulatory frameworks that govern it.
The Ethical Compass of Media
Media ethics are the moral principles that guide the behavior of individuals and organizations involved in the communication process. These principles encompass truthfulness, accuracy, fairness, impartiality, and respect for privacy. In an era of fake news, clickbait, and filter bubbles, adhering to these principles is more crucial than ever.
Journalists, for instance, are expected to uphold the highest standards of accuracy and objectivity. Social media influencers must be transparent about sponsored content and avoid misleading their audience. Broadcasters have a responsibility to present balanced news coverage and protect the privacy of individuals.
The Role of Regulation
Media regulation is the system of rules and standards imposed on the media by government bodies. Its purpose is to protect the public interest, promote diversity, and maintain order. However, the balance between free speech and regulation is a delicate one.
Over-regulation can stifle creativity and innovation, while under-regulation can lead to abuses of power and harm to the public. Finding the right equilibrium is a complex challenge.
Challenges and Opportunities
The digital age has presented both challenges and opportunities for media ethics and regulation. On the one hand, the internet has democratized information, giving a voice to marginalized groups. On the other hand, it has facilitated the spread of misinformation and hate speech.
New technologies like artificial intelligence and deepfakes raise additional ethical questions. As media continues to evolve, so too must our understanding of ethics and regulation.
Ultimately, the responsibility for ethical media lies not just with media organizations but also with the public. By being critical consumers of information and holding media outlets accountable, we can contribute to a more ethical and informed media landscape.
Conclusion

Media, in its myriad forms, is the lifeblood of modern society. It’s the conduit through which information flows, shaping opinions, influencing cultures, and driving economies. From the ancient storyteller to the digital influencer, media has evolved dramatically, yet its core function of connecting people and disseminating knowledge remains constant.
However, the power of media is a double-edged sword. It can be a force for good, informing, educating, and entertaining. But it can also misinform, manipulate, and divide. To harness its potential fully, a critical understanding of media is essential. By developing media literacy, we can navigate this complex landscape with discernment, ensuring that media serves as a tool for empowerment rather than control.
Ultimately, media is a reflection of society, and its future depends on how we use it.
Read more:
- How to Get the Rare Tesla Tequila?
- What is Amazon’s GPT44x and How Does It Work?
- Blueface Net Worth, Lifestyle And Updates In 2024
Featured Image source: https://tinyurl.com/eju94zyh

